The cryptocurrency ecosystem stands at a critical crossroads. On one side, we have institutional control—where established financial entities manage digital assets on behalf of users. On the other, individual self-custody—where users maintain complete sovereignty over their private keys. This fundamental dichotomy isn’t just a technical preference; it represents contrasting philosophies about financial freedom, security, and trust in the digital age.
Recent regulatory developments have intensified this divide. The U.S. Justice Department’s shift in enforcement strategy, European states’ push for encryption backdoors, and evolving financial regulations are reshaping how we think about who should control our digital assets. Understanding this tension is essential for anyone navigating the increasingly complex world of cryptocurrency ownership.
Key Takeaways: The Custody Decision
- The choice between institutional control and self-custody fundamentally determines who has access to your digital assets
- Self-custody offers complete control but requires technical knowledge and introduces single-point-of-failure risks
- Institutional custody provides convenience and familiarity but creates dependency on third parties
- Regulatory approaches vary globally, with some jurisdictions pushing for greater surveillance of digital assets
- The ideal approach depends on your technical comfort, risk tolerance, and philosophical stance on financial sovereignty
- Hybrid models are emerging that attempt to balance control with convenience
Understanding the Custody Spectrum
Custody in the cryptocurrency context refers to who controls the private keys that provide access to digital assets. Unlike traditional financial systems where banks act as trusted intermediaries, cryptocurrency’s architecture allows for direct ownership without middlemen. This creates a spectrum of custody options:
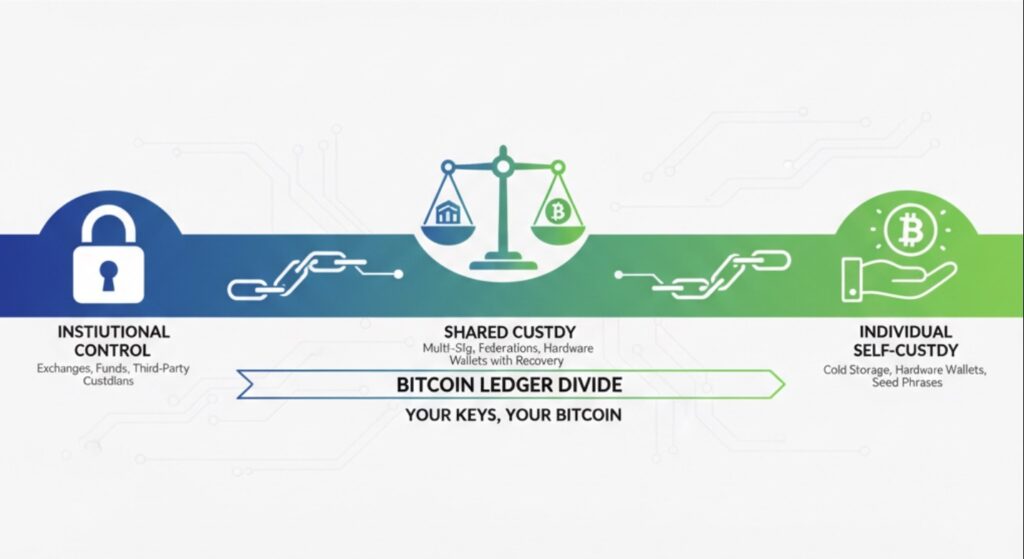
Full Institutional Control
Exchanges, banks, and custodians hold your private keys. You access assets through their platforms, similar to traditional banking.
Collaborative Custody
Multi-signature or shared custody arrangements where control is distributed between you and trusted institutions.
Complete Self-Custody
You maintain exclusive control of your private keys, typically using hardware wallets or secure software solutions.
The decision between these models isn’t merely technical—it reflects your stance on trust, security, and financial autonomy. As regulatory pressures mount globally, this decision becomes increasingly consequential.
Institutional Control: The Convenience Proposition
Institutional custody solutions offer a familiar model for those accustomed to traditional financial services. These entities—ranging from cryptocurrency exchanges to specialized custodians like BitGo—manage private keys on behalf of their clients, providing a layer of professional security and operational convenience.

The Institutional Control Framework
Institutional custody operates through a structured framework designed to balance security with accessibility:
| Component | Implementation | User Impact |
| Key Management | Cold storage with multi-signature authorization | No direct key access; dependent on institution’s security |
| Access Control | Identity verification, 2FA, withdrawal limits | Potential delays during high-security procedures |
| Regulatory Compliance | KYC/AML procedures, transaction monitoring | Reduced privacy, potential asset freezes |
| Insurance | Third-party coverage for certain risks | Partial protection against institutional failure |
Advantages of Institutional Control
- Simplified user experience with familiar login processes
- Professional security infrastructure and expertise
- Recovery options if access credentials are lost
- Potential insurance coverage against certain losses
- Integrated financial services (trading, lending, staking)
- Reduced technical burden on the user
Disadvantages of Institutional Control
- Single point of failure if the institution is compromised
- Exposure to counterparty risk (insolvency, fraud)
- Potential withdrawal restrictions during market stress
- Reduced privacy due to KYC requirements
- Vulnerability to regulatory changes and asset freezes
- Contradicts the “not your keys, not your coins” principle
Historical Perspective: The collapse of Mt. Gox in 2014, which lost approximately 850,000 Bitcoin (7% of all Bitcoin at the time), serves as a stark reminder of institutional custody risks. This event sparked the popular crypto mantra: “Not your keys, not your coins.”
Individual Self-Custody: The Sovereignty Solution
Self-custody represents the purest expression of cryptocurrency’s original vision—financial sovereignty without intermediaries. By maintaining exclusive control of your private keys, you eliminate dependency on third parties but assume full responsibility for security and access management.

The Self-Custody Infrastructure
Effective self-custody requires a thoughtful approach to security and redundancy:
Hardware Components
- Hardware Wallets: Dedicated devices that store private keys offline, protecting them from online threats
- Seed Phrase Backups: Physical records of recovery phrases, typically 12-24 words that can restore wallet access
- Secure Storage: Fireproof safes, safety deposit boxes, or distributed storage locations for backups
Knowledge Requirements
- Technical Understanding: Basic knowledge of blockchain operations and security principles
- Security Practices: Awareness of common threats and appropriate countermeasures
- Recovery Procedures: Familiarity with wallet restoration processes in case of device failure
Advantages of Self-Custody
- Complete control over your digital assets
- Immunity to exchange hacks and institutional failures
- Enhanced privacy with no mandatory KYC
- Freedom from withdrawal limits or freezes
- Direct blockchain interaction without intermediaries
- Alignment with cryptocurrency’s decentralization ethos
Disadvantages of Self-Custody
- Full responsibility for security and key management
- Risk of permanent loss if keys or recovery phrases are lost
- Technical learning curve for proper implementation
- Limited recourse in case of user error or theft
- Potential inheritance complications
- Increased physical security concerns as holdings grow
Critical Warning: An estimated 20% of all Bitcoin (approximately 4 million BTC) is permanently lost, often due to misplaced seed phrases, damaged devices, or forgotten PINs. Self-custody requires meticulous attention to backup procedures and security practices.
The Evolving Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory environment surrounding cryptocurrency custody is rapidly evolving, with significant implications for both institutional and self-custody approaches. Government attitudes range from supportive to hostile, creating a complex global patchwork of rules.
Key Regulatory Developments
United States
The U.S. approach focuses on integrating cryptocurrencies into existing financial frameworks. The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) is implementing the GENIUS Act, which applies Bank Secrecy Act obligations to stablecoin issuers while exploring innovative monitoring technologies.
European Union
Several European states are pursuing encryption backdoors that could fundamentally compromise the security underpinning self-custody. France’s “Narcotrafic” law amendment and the EU’s “chat control” initiative represent direct challenges to cryptographic privacy.
Global South
Many developing nations are taking a more permissive approach to cryptocurrency self-custody, recognizing its potential for financial inclusion. However, institutional frameworks remain underdeveloped, creating regulatory uncertainty.
“The institutional imperative is not to halt this evolution but to harness it and bring it under the purview of existing financial control mechanisms. The emphasis on artificial intelligence and blockchain monitoring reveals a deeper understanding that the key to managing this space is not through prohibition but through the ‘on-ramping’ of these technologies into the traditional system.”
These regulatory developments create tension between institutional adoption and individual sovereignty. As governments develop more sophisticated monitoring capabilities, the technical barriers to effective self-custody may increase, potentially pushing more users toward regulated institutional solutions.
Making Your Custody Decision: A Framework
Choosing between institutional control vs individual self-custody requires balancing multiple factors including security needs, technical comfort, philosophical alignment, and practical considerations. This decision framework can help guide your approach:
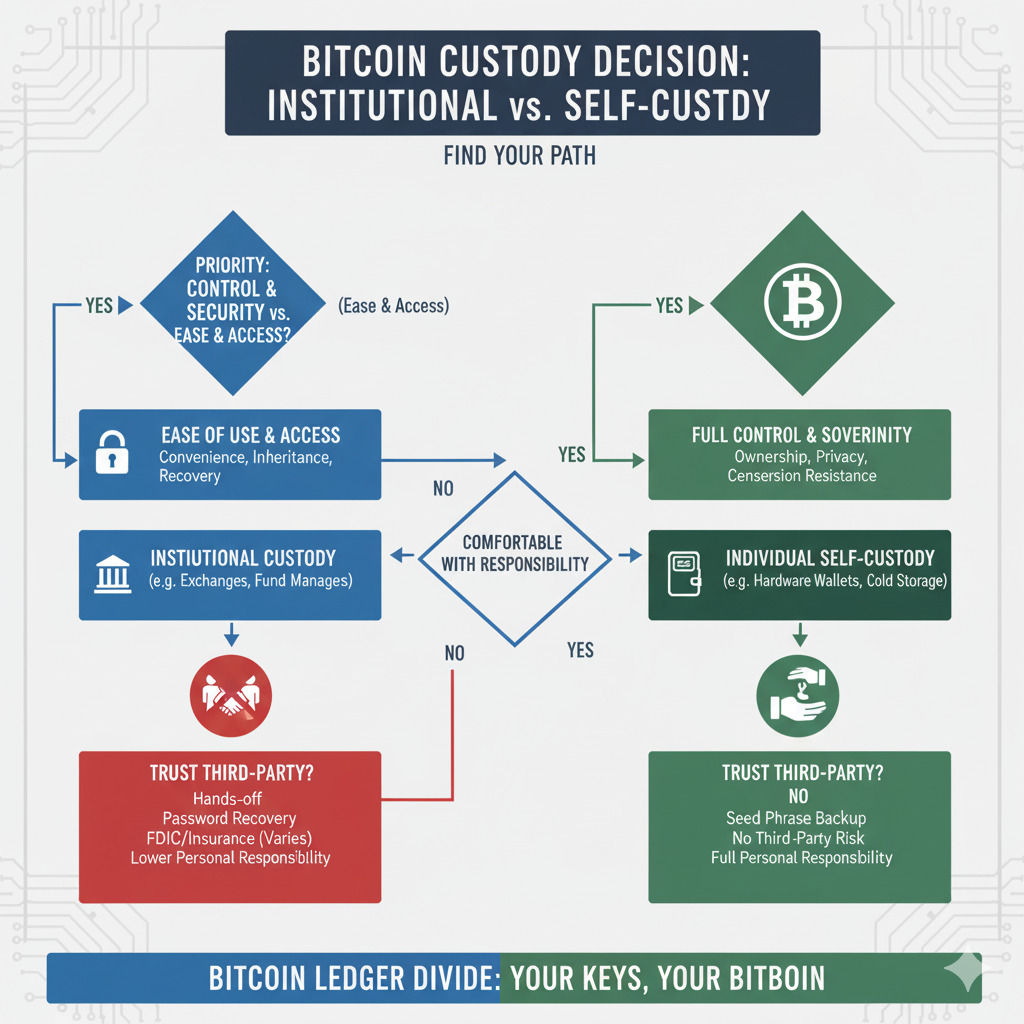
- You prioritize convenience over complete control
- You lack technical confidence to manage keys securely
- You require integrated financial services (trading, lending)
- You value recovery options if access credentials are lost
- You prefer familiar interfaces and customer support
- You need straightforward inheritance planning
Consider Institutional Control If:
- You value complete control over your assets
- You have technical knowledge to manage security
- You prioritize privacy and minimal KYC requirements
- You’re concerned about institutional counterparty risk
- You align philosophically with cryptocurrency’s decentralized ethos
- You want immunity from arbitrary withdrawal restrictions
Consider Self-Custody If:
- You want to balance control with convenience
- You prefer distributing risk across multiple solutions
- You have varying needs for different portions of your holdings
- You seek collaborative custody with trusted parties
- You want institutional-grade security with personal oversight
- You’re gradually building technical knowledge
Consider Hybrid Approaches If:
Need Personalized Custody Guidance?
Our team of experts can help you develop a custody strategy tailored to your specific needs, risk tolerance, and technical comfort level. Schedule a consultation to discuss your options.
Future Trends in the Custody Landscape
The dichotomy between institutional control and individual self-custody continues to evolve as technology advances and regulatory frameworks mature. Several emerging trends are reshaping this landscape:
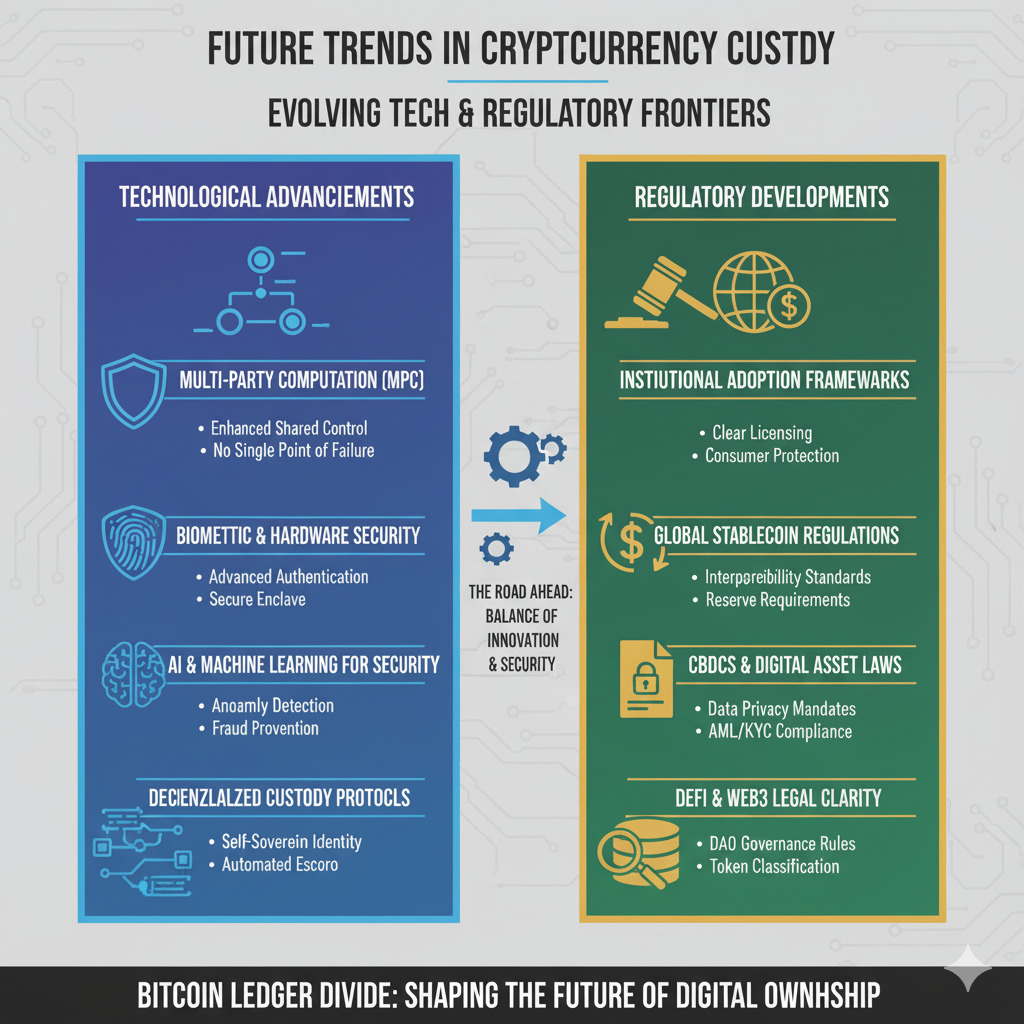
Multi-Institution Custody
Hybrid models that distribute control across multiple institutions are gaining traction, offering enhanced security through decentralization while maintaining service integration. These solutions use multi-signature technology to prevent single points of failure.
Privacy-Preserving Compliance
Advanced cryptographic techniques like zero-knowledge proofs are enabling compliance without compromising privacy. These technologies allow users to prove regulatory compliance without revealing sensitive information, potentially bridging the gap between institutional requirements and self-custody principles.
User-Friendly Self-Custody
The technical barriers to effective self-custody are decreasing as hardware and software solutions become more intuitive. Social recovery systems, simplified interfaces, and better backup mechanisms are making self-custody accessible to less technical users.
Emerging Solution: Multi-institution custody (MIC) represents a promising middle ground, combining control and resilience without the burdens of pure self-custody or the trust dependencies of traditional custodians. This approach distributes custody across multiple institutions, eliminating single points of failure while maintaining service integration.
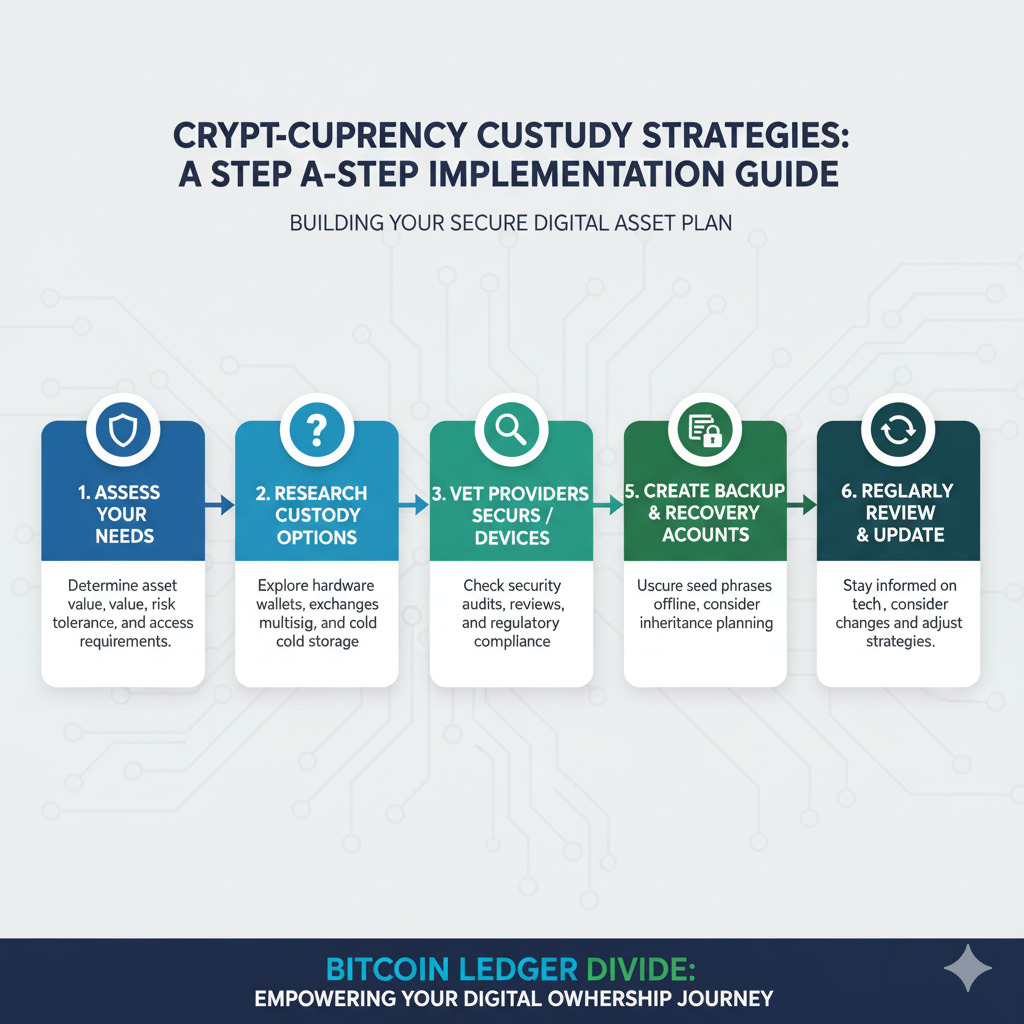
Practical Steps: Implementing Your Custody Strategy
Whether you choose institutional control, individual self-custody, or a hybrid approach, implementing your decision requires careful planning and execution. Here are practical steps to consider:
-
Assess Your Needs and Risk Profile
Evaluate your technical comfort, holdings size, privacy requirements, and service needs to determine which custody approach aligns with your situation.
-
Start With Education
Before implementing any custody solution, invest time in understanding the technical fundamentals, security best practices, and potential vulnerabilities.
-
Test With Small Amounts
Begin your implementation with non-critical funds to gain comfort with the processes and interfaces before committing significant assets.
-
Document Your Procedures
Create clear documentation of your custody setup, including access methods, recovery procedures, and contingency plans for various scenarios.
-
Implement Redundancy
Regardless of your chosen approach, build redundancy into your system to protect against hardware failure, service outages, or other disruptions.
Get Our Comprehensive Custody Implementation Guide
Our detailed guide covers everything from security best practices to step-by-step setup instructions for both institutional and self-custody approaches. Download it now to start building your secure custody strategy.
Conclusion: Navigating the Digital Ledger Divide
The dichotomy between institutional control vs individual self-custody represents more than a technical choice—it reflects fundamental values about financial sovereignty, trust, and security in the digital age. As regulatory pressures mount and technology evolves, this divide will continue to shape the cryptocurrency landscape.
There is no universal “right answer” to the custody question. The optimal approach depends on your specific circumstances, technical capabilities, risk tolerance, and philosophical alignment. Many users find that a thoughtful combination of approaches—perhaps using self-custody for long-term holdings and institutional solutions for active trading—provides the best balance.
What remains clear is that understanding the implications of your custody choice is essential. Whether you entrust your assets to an institution or take full control through self-custody, doing so with complete awareness of the trade-offs ensures your decision aligns with your broader financial goals and values.

Ready to Optimize Your Custody Strategy?
Our team of experts specializes in creating personalized custody solutions that balance security, convenience, and control. Whether you’re new to cryptocurrency or managing significant holdings, we can help you navigate the complexities of the digital asset landscape.