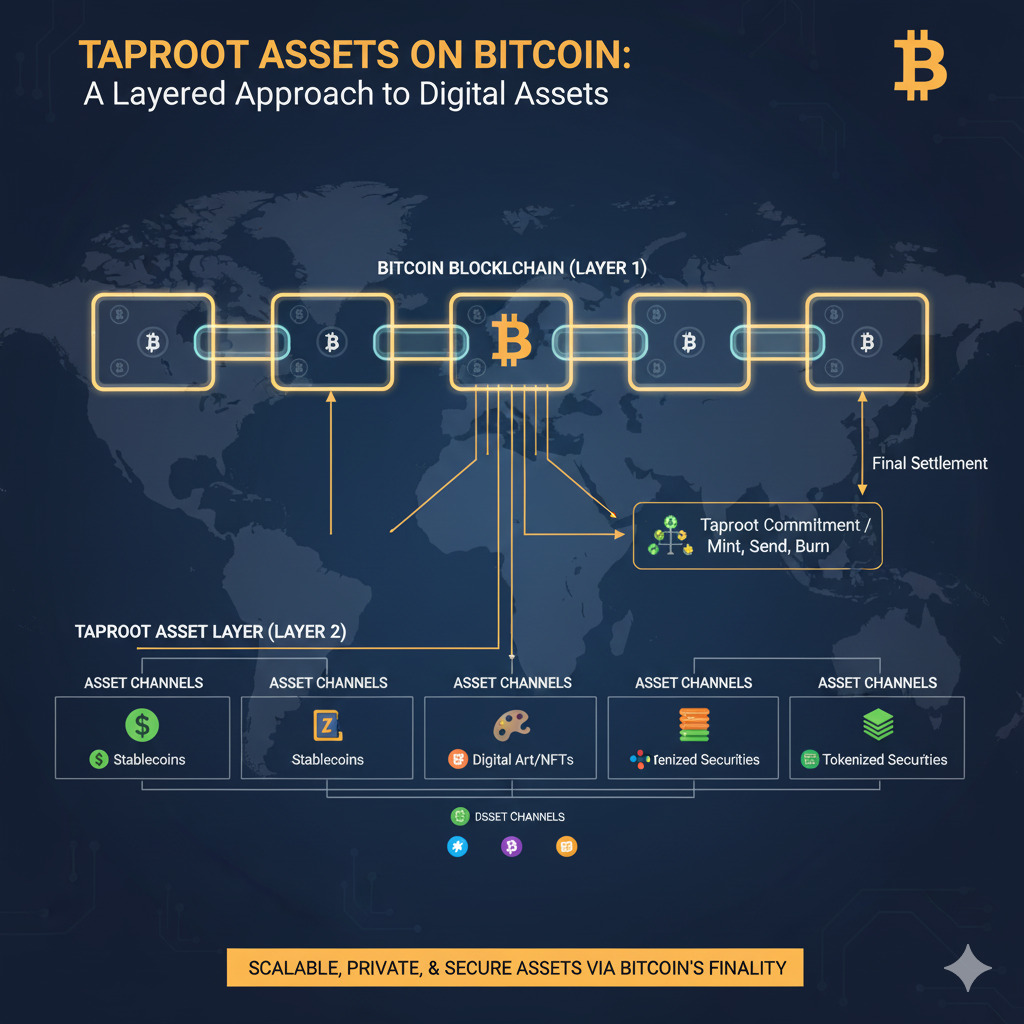
Taproot Assets represents a significant evolution in Bitcoin’s capabilities, enabling the issuance of digital assets directly on the world’s most secure blockchain. This protocol leverages Bitcoin’s Taproot upgrade to create a scalable framework for tokens while maintaining the network’s foundational security and decentralization principles. As major players like Tether begin integrating their stablecoins via this protocol, we’re witnessing Bitcoin’s transformation from a single-asset monetary network into a versatile multi-asset platform.
What Is Taproot Assets Protocol?
Taproot Assets is a protocol that allows users to issue digital assets on the Bitcoin blockchain. These assets can be fungible tokens like stablecoins or non-fungible tokens like collectibles. The protocol was introduced by Lightning Labs in 2022 (previously known as Taro) and represents a significant advancement in Bitcoin’s functionality without requiring changes to the base layer.
Unlike general-purpose platforms such as Ethereum with its Turing-complete smart contracts, Taproot Assets maintains Bitcoin’s minimalist approach, prioritizing security and efficiency for token issuance rather than introducing complex programmability. This design philosophy aligns with Bitcoin’s core values of reliability and security.
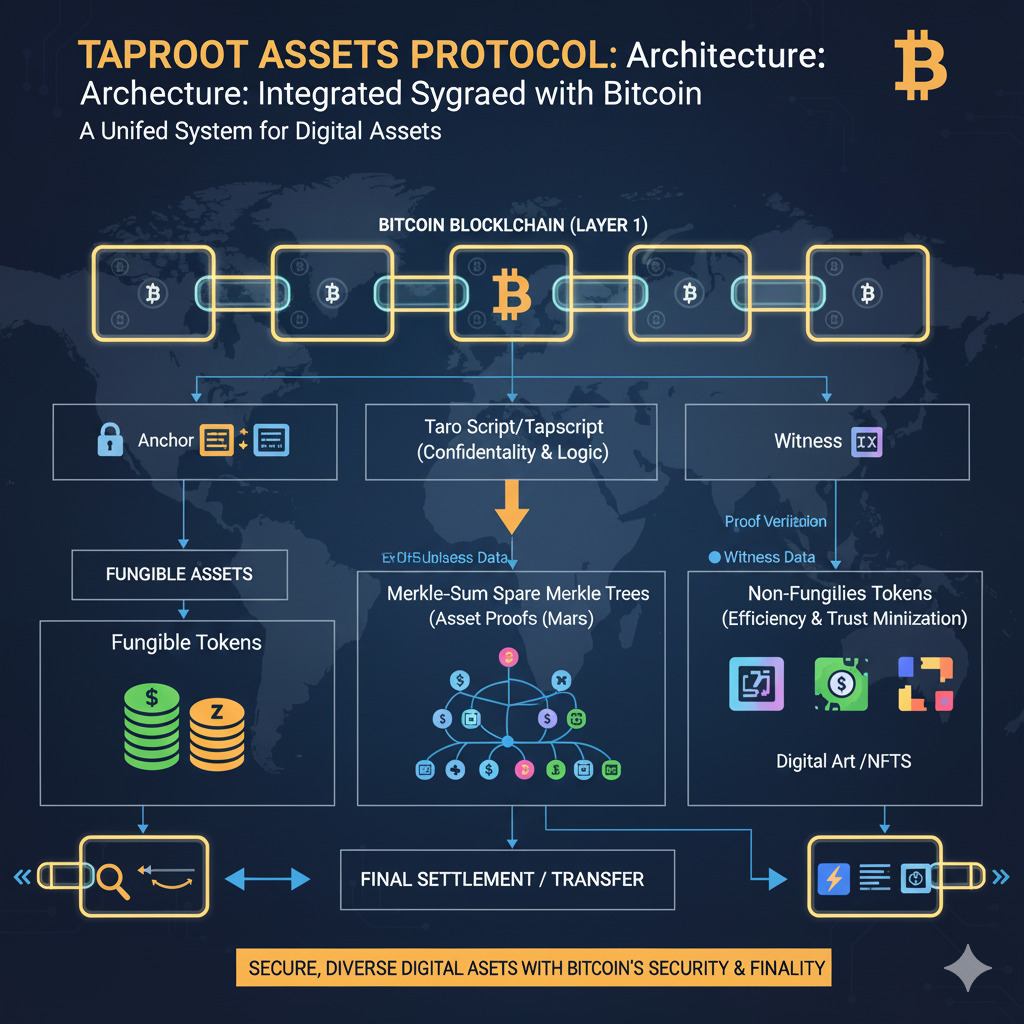
Technical Architecture of Taproot Assets
The Taproot Assets Protocol leverages several advanced cryptographic concepts to enable efficient asset issuance and transfer on Bitcoin. Understanding these technical components is essential for developers and enthusiasts looking to work with this protocol.
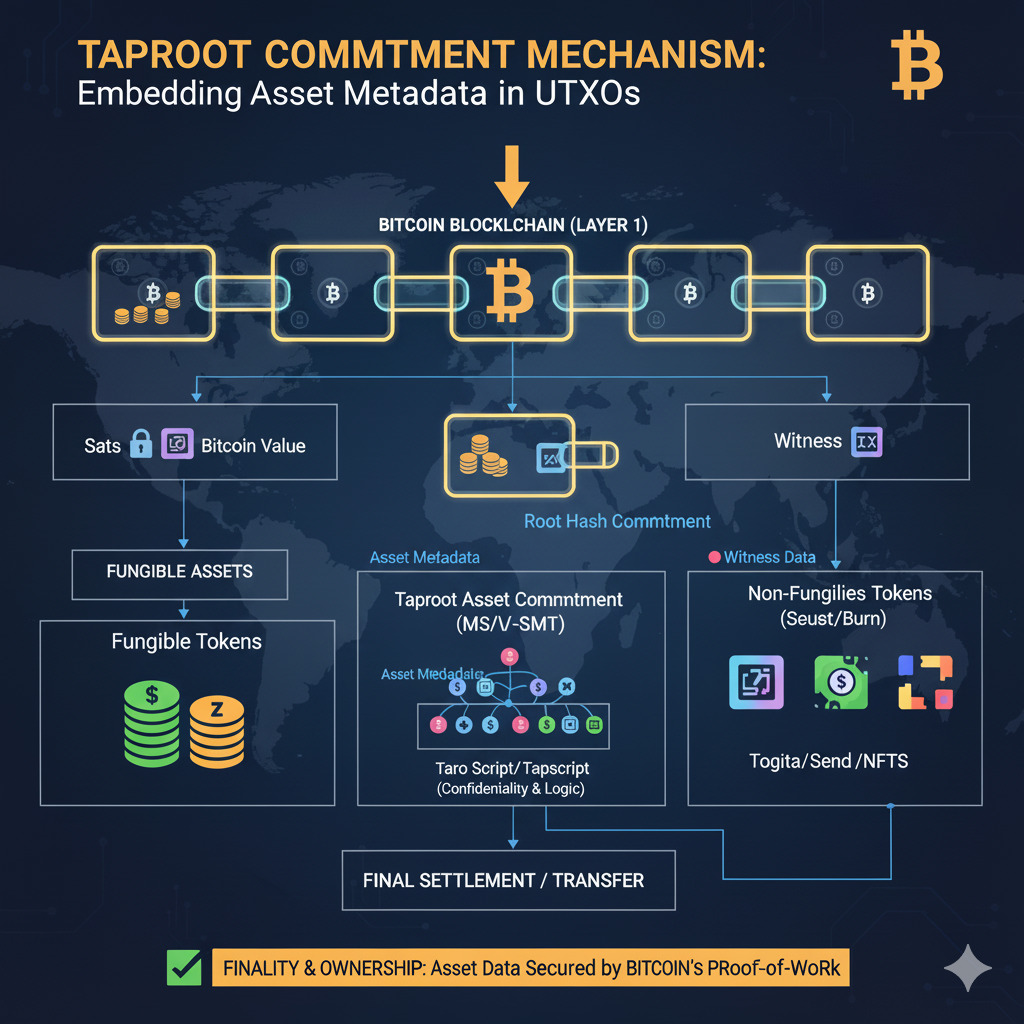
Taproot Commitment Mechanism
Taproot Assets utilizes the 2021 Taproot upgrade to embed asset metadata within existing Bitcoin Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs). This approach drastically reduces the on-chain data footprint compared to alternative token implementations. The protocol uses Taproot’s Merkelized Alternative Script Trees (MAST) to commit new assets and transfers efficiently within a single Bitcoin UTXO.
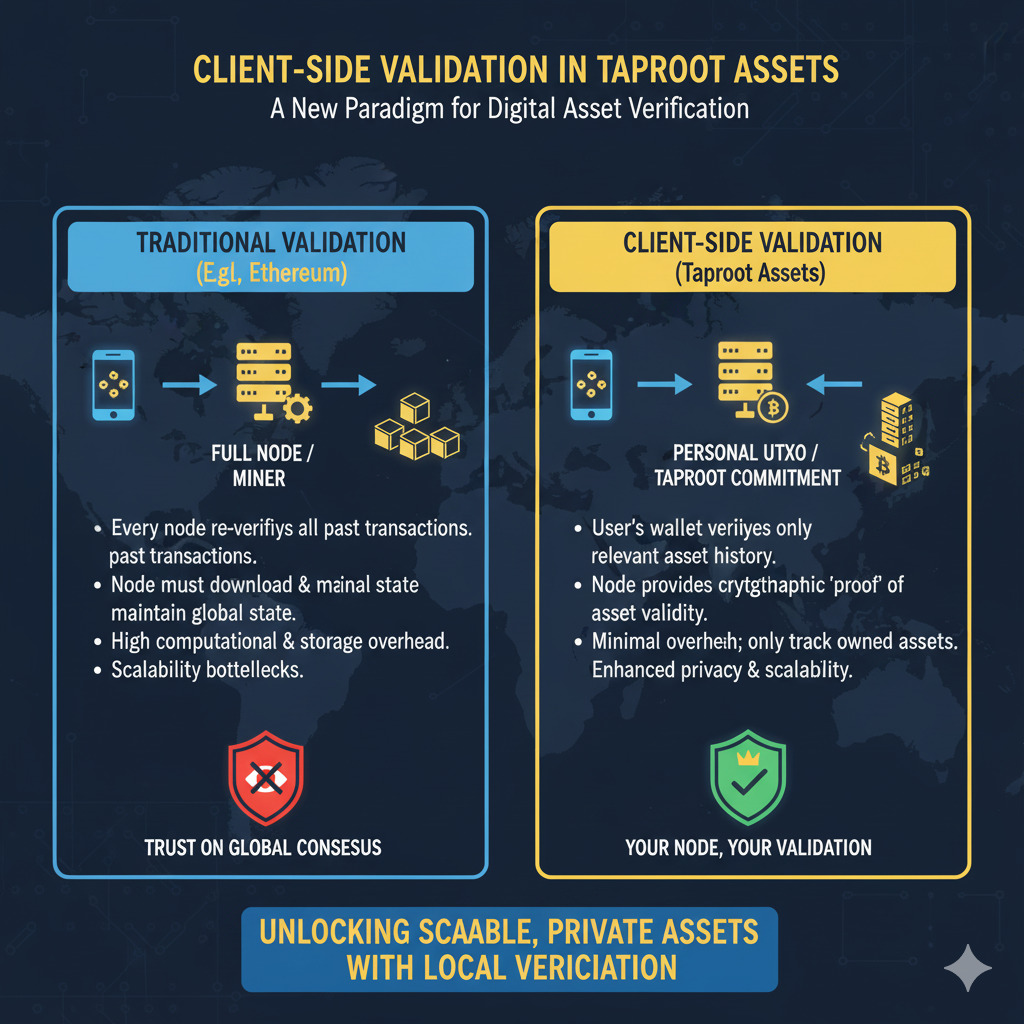
Client-Side Validation
Unlike traditional blockchain tokens that require global consensus verification, Taproot Assets employs Client-Side Validation (CSV). This means the asset’s validity is verified by the asset holder and transacting parties, independent of Bitcoin’s global consensus rules. This approach shifts storage and verification costs off-chain, enabling greater scalability without burdening the Bitcoin network.
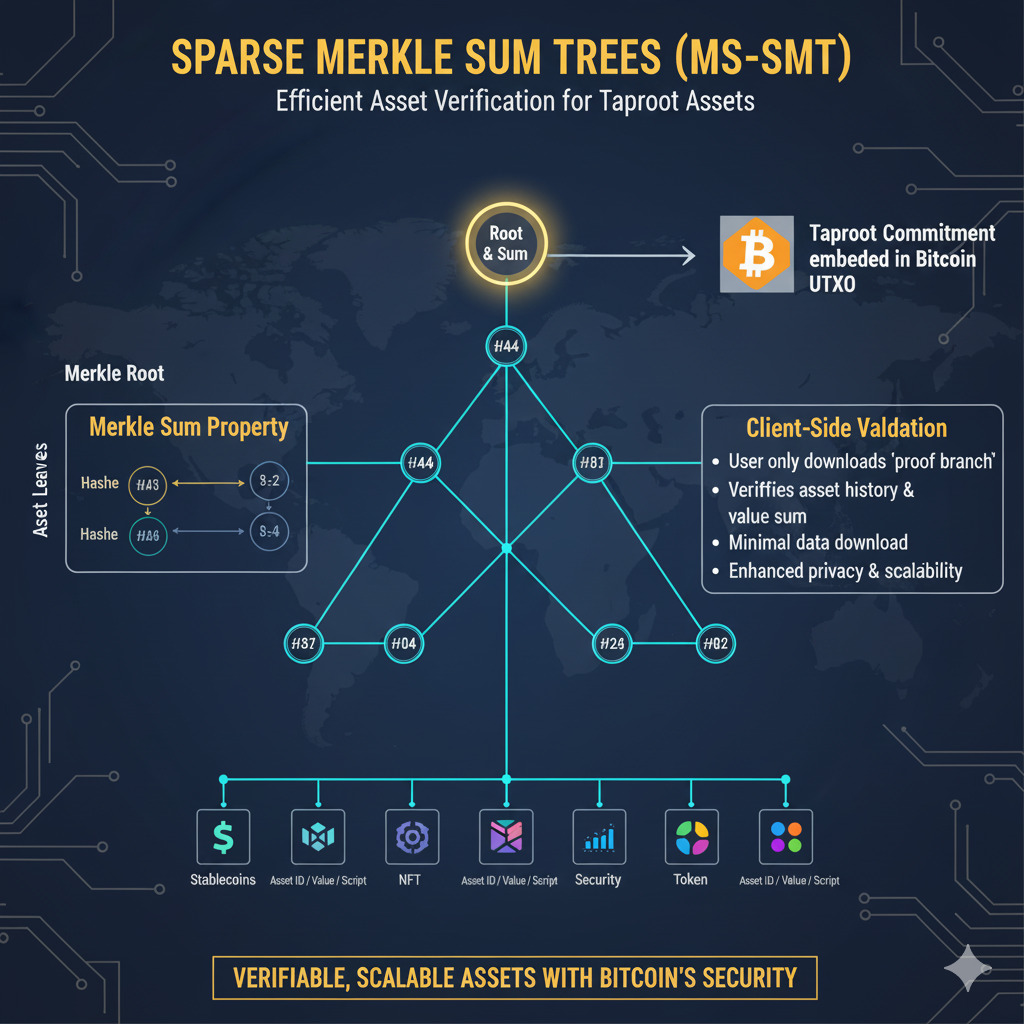
Sparse Merkle Sum Trees
Security and non-inflation of assets are proven using Sparse Merkle Sum Trees (MSTs). The root of this structure is embedded in the Taproot tapscript, serving as the secure on-chain anchor that ensures the total asset quantity has not been inflated since its genesis. This cryptographic structure allows efficient verification of asset transfers while maintaining a minimal on-chain footprint.
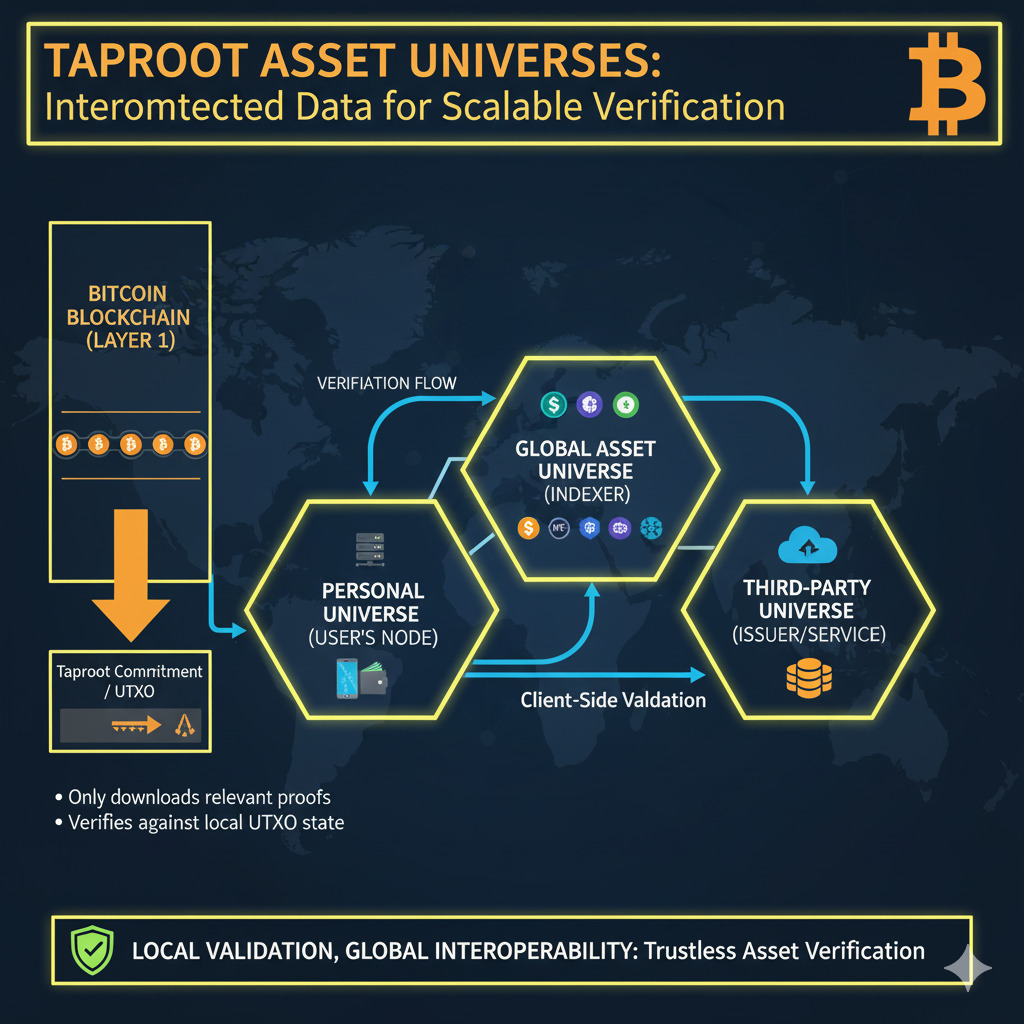
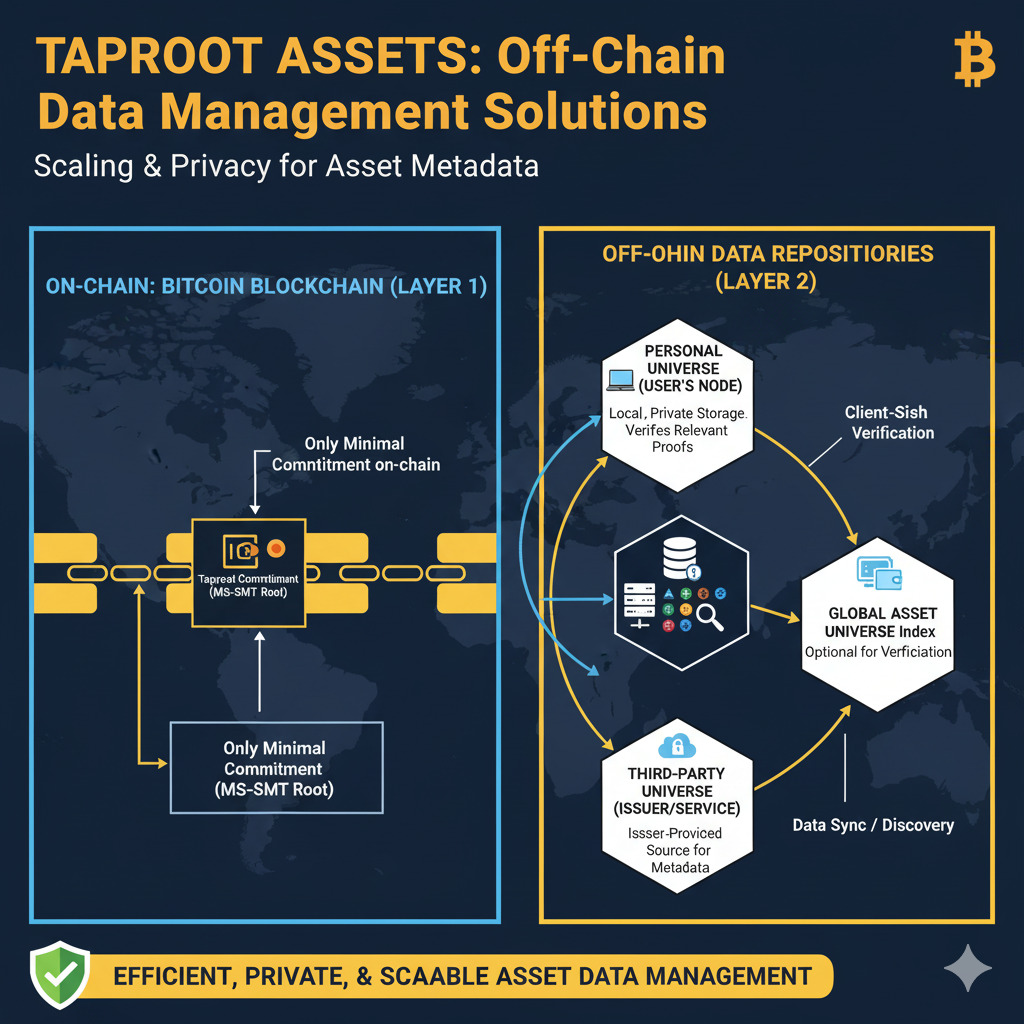
Taproot Asset Universes
“Universes” are repositories that store essential off-chain witness data, proofs, and asset metadata. These are typically run by the asset issuer or providers using the tapd daemon. Users must access a Universe to validate an asset’s transfer history and lineage for client-side verification.
Think of Universes as similar to GitHub repositories for asset history – they maintain the complete record of an asset’s existence and movements without requiring this data to be stored on the Bitcoin blockchain itself. This separation of concerns allows for efficient scaling while maintaining security.
Want to Learn More About Bitcoin Protocol Development?
Stay updated on the latest innovations in Bitcoin technology, including Taproot Assets, Lightning Network advancements, and more. Join our technical newsletter for in-depth analysis and implementation guides.
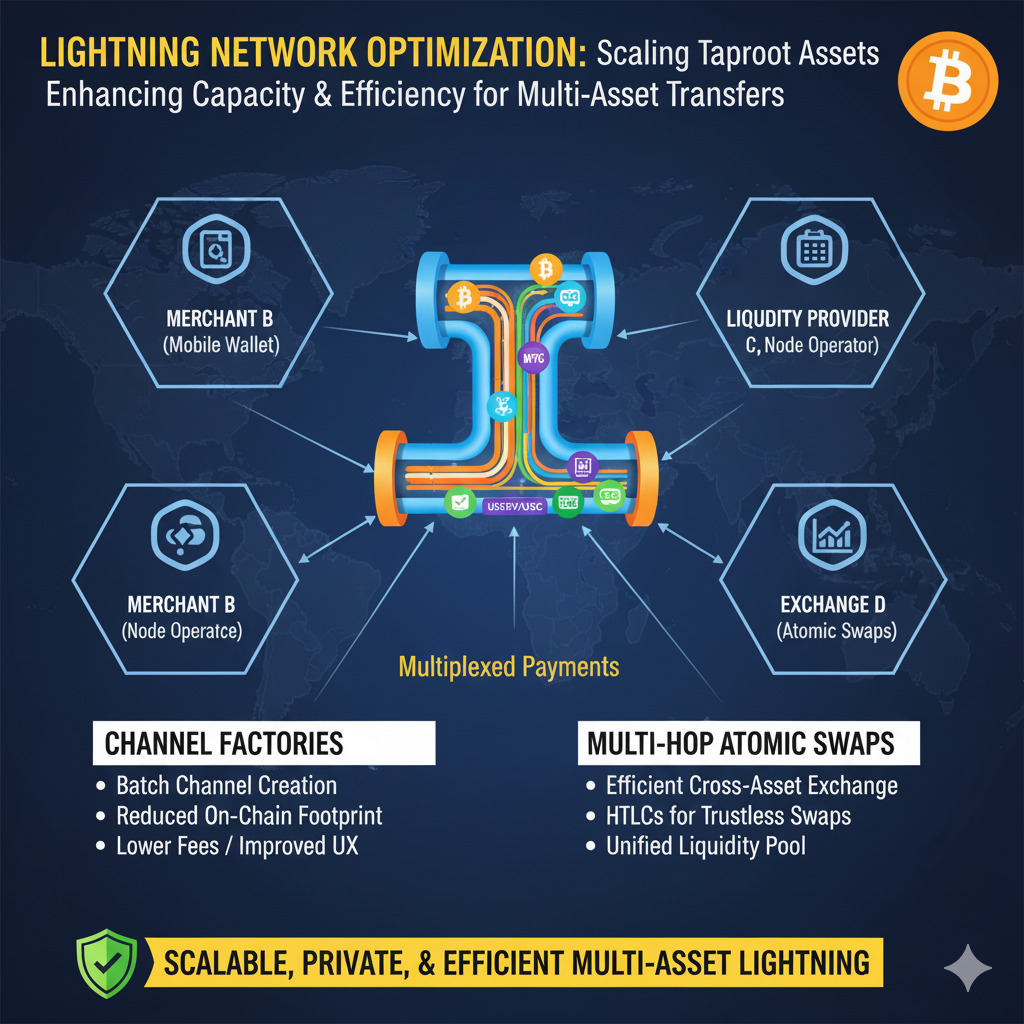
Lightning Network Integration
One of the most powerful aspects of Taproot Assets is its native integration with the Lightning Network, enabling instant, low-cost transfers of issued assets. This integration transforms how assets can move within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
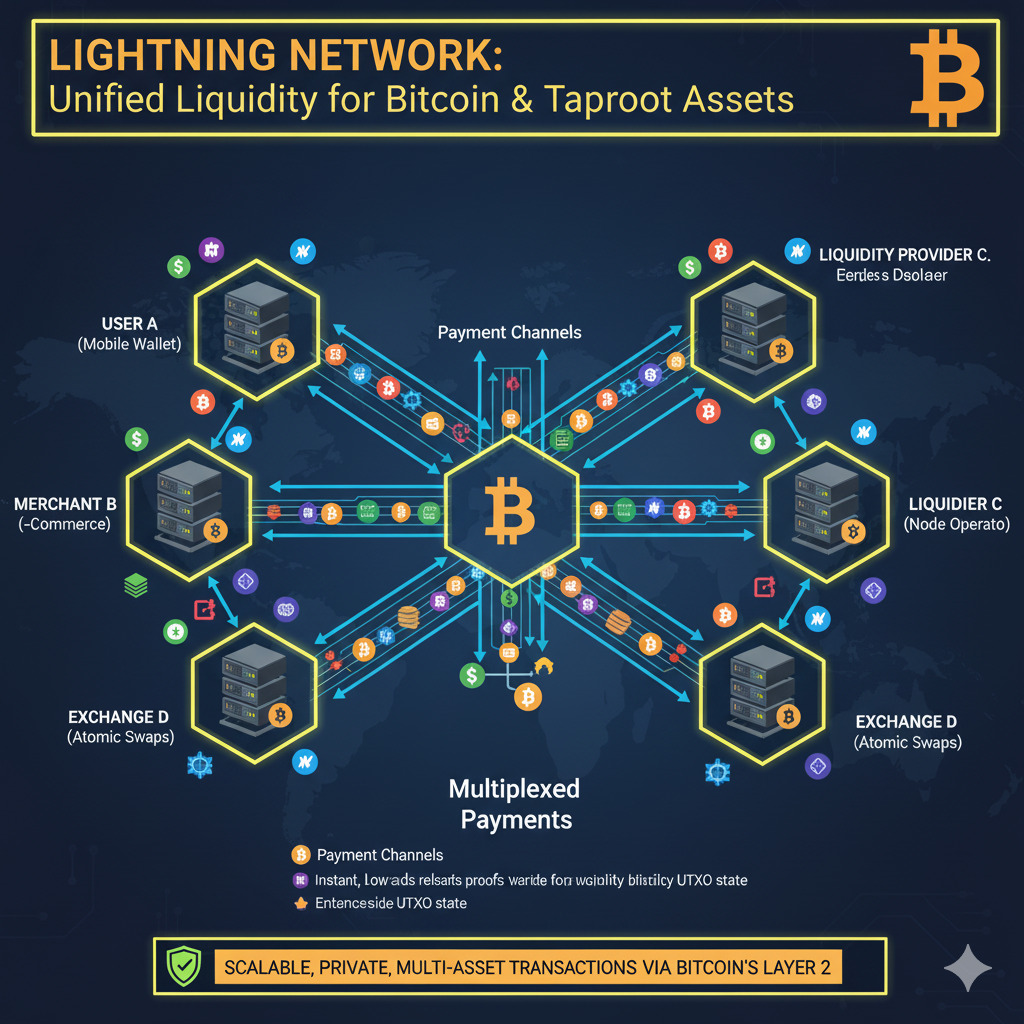
Multi-Asset Channels
Taproot Assets was engineered to use the Lightning Network as its primary distribution rail. Assets can be deposited into existing Lightning channels and transferred instantly with minimal fees. Channels can efficiently carry both BTC and Taproot Assets within the same UTXO, maximizing efficiency and minimizing chain footprint.
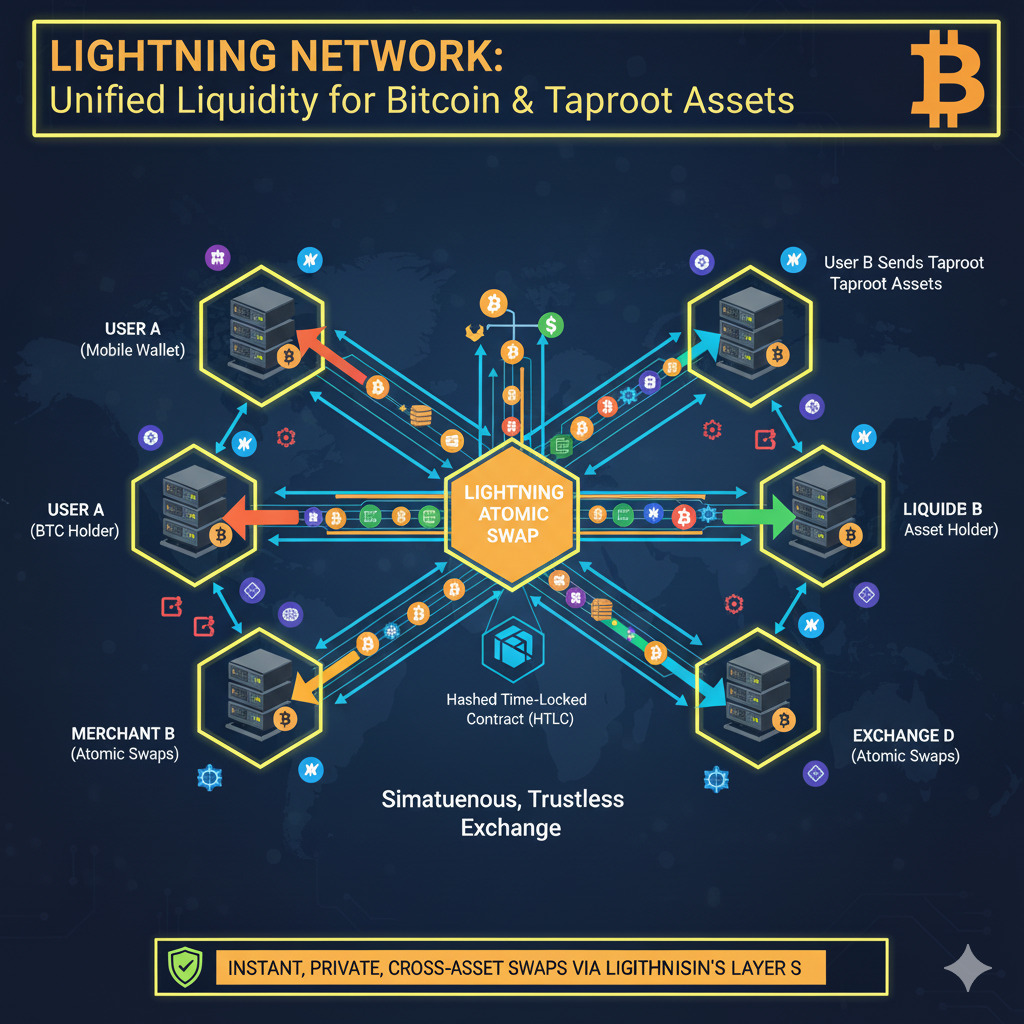
Atomic Swaps and Brokerage
The Lightning Network integration transforms the network into a brokerage system. It enables atomic conversions between Taproot Assets (like stablecoins) and Bitcoin within the channel structure. This allows a Taproot Asset invoice to be seamlessly settled using BTC, or vice versa, creating a fluid multi-asset ecosystem.
Economic Incentives for Node Operators
This multi-asset capability creates compelling economic incentives for Lightning Network routing node operators. They can earn increased routing fees (paid in satoshis) by facilitating atomic swaps and multi-asset transfers. This alignment of incentives helps strengthen the Lightning Network infrastructure while supporting the Taproot Assets ecosystem.
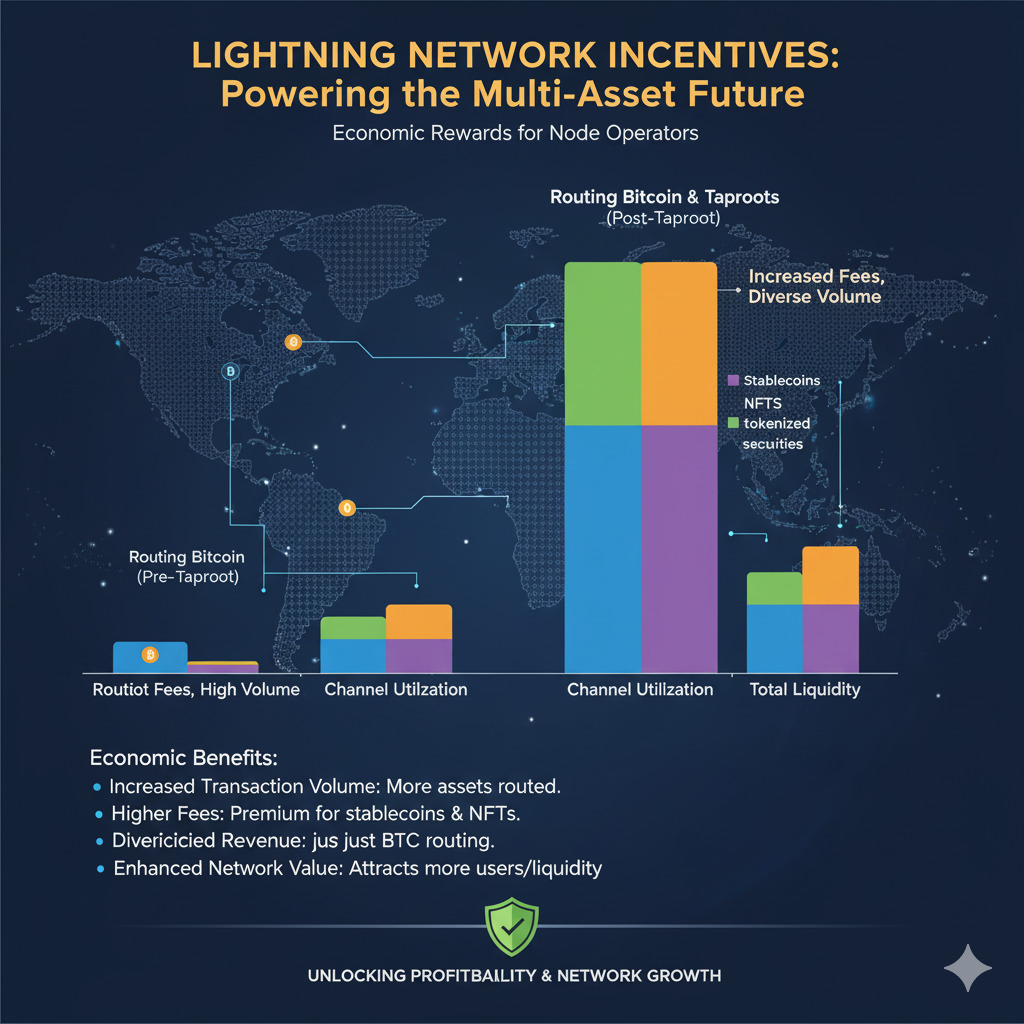
Scaling Challenges and Solutions
While Taproot Assets represents a significant advancement in Bitcoin’s capabilities, several scaling challenges must be addressed for widespread adoption. The Lightning Network’s ability to handle massive transaction volumes comparable to competing chains like Solana or Tron remains a key challenge.
Channel Optimization
The Lightning Network is evolving to meet increasing demand, with smaller channels closing in favor of larger, more streamlined channels. This optimization improves payment success rates for larger transfers and reduces the overall number of on-chain transactions needed to maintain the network.
Off-Chain Data Management
Managing off-chain data efficiently is crucial for Taproot Assets’ success. The protocol’s Universe repositories must be reliable and accessible while maintaining decentralization principles. Various approaches to data availability are being explored, including distributed storage solutions and incentivized data hosting.
Advantages of Taproot Assets
- Leverages Bitcoin’s security and stability
- Minimal on-chain footprint
- Lightning Network compatibility for instant transfers
- No changes required to Bitcoin’s base layer
- Supports both fungible and non-fungible assets
- Client-side validation reduces network burden
Challenges to Address
- Off-chain data availability requirements
- Lightning Network channel capacity limitations
- Education barrier for users and developers
- Competition from other Bitcoin asset protocols
- Regulatory uncertainty for issued assets
- Early-stage technology still being tested
Regulatory Landscape for Taproot Assets
As assets like stablecoins move to Taproot Assets on Bitcoin, regulatory considerations become increasingly important. The EU’s Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) is particularly relevant, as it treats stablecoins as Asset-Reference Tokens (ARTs) with strict requirements for transparency, disclosure, and backing.
Taproot Assets’ design may actually help issuers comply with these regulations. The protocol’s transparent nature, combined with Bitcoin’s immutable ledger, provides a strong foundation for audit trails and verification of asset backing. However, issuers will still need to ensure their specific implementations meet regulatory requirements in their jurisdictions.
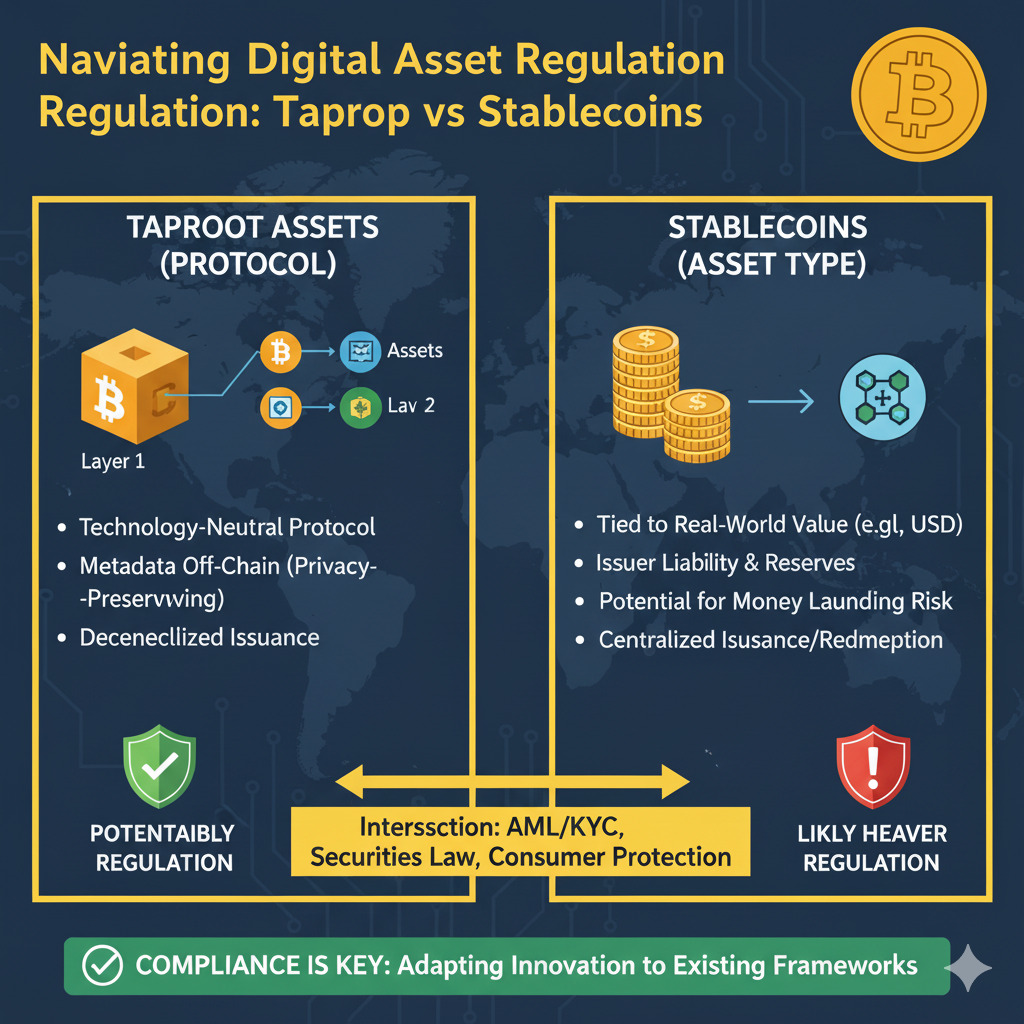
Future Outlook for Taproot Assets
The Taproot Assets Protocol is still in its early stages, with significant developments on the horizon. Future roadmap items include enhanced privacy features like confidential transactions and zero-knowledge proofs, as well as expanded support for complex asset types and governance structures.
Decentralized Finance on Bitcoin
Taproot Assets could enable a new wave of decentralized finance applications built directly on Bitcoin. While these won’t match the programmability of Ethereum-based DeFi, they could offer unique advantages in security, stability, and Lightning Network integration. The potential for a decentralized foreign exchange market running on Bitcoin nodes represents a particularly compelling use case.

Ecosystem Development
Developer enthusiasm for Taproot Assets is accelerating, leading to the creation of essential infrastructure components. Open-source SDKs and self-custodial mobile wallets like Joltz are emerging, enabling multi-asset payments and trustless swaps on the Lightning Network. This growing ecosystem will be crucial for mainstream adoption.

Competition with Other Protocols
Taproot Assets isn’t the only protocol bringing assets to Bitcoin. Its main competitor in Client-Side Validation is the RGB protocol, which aims for highly expressive, Turing-complete smart contracts and utilizes a different commitment structure. This healthy competition will likely drive innovation across the Bitcoin ecosystem.
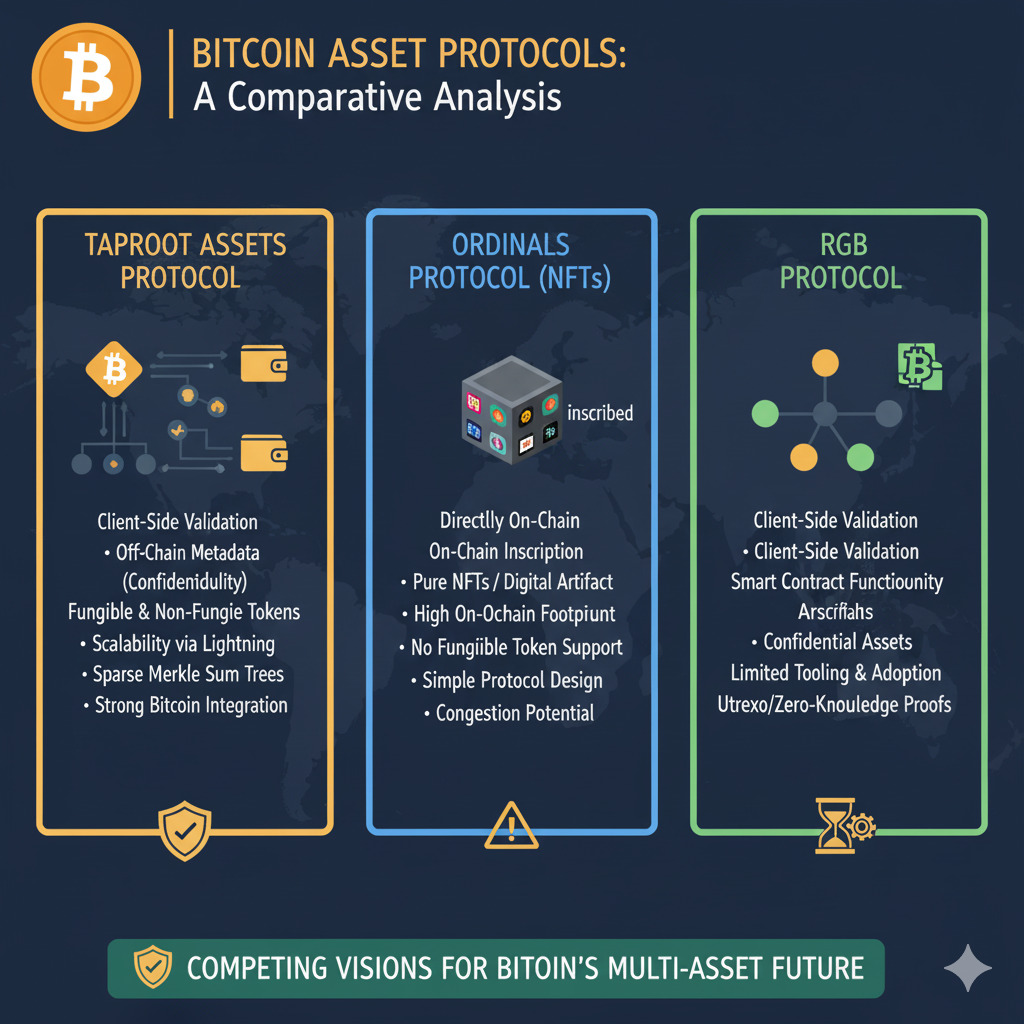
Conclusion: Bitcoin’s Evolution Through Taproot Assets
Taproot Assets represents a significant milestone in Bitcoin’s evolution from a single-asset network to a multi-asset platform. By leveraging the security and stability of Bitcoin while enabling new asset types and use cases, this protocol expands Bitcoin’s utility without compromising its core principles.
As major players like Tether begin issuing assets on Taproot Assets, we’re likely to see accelerated adoption and ecosystem growth. The combination of Bitcoin’s security with Lightning Network’s speed creates a compelling foundation for the next generation of digital assets.
For developers, investors, and Bitcoin enthusiasts, now is the time to understand and engage with this transformative technology. The future of Bitcoin is expanding beyond digital gold, and Taproot Assets is helping to write that next chapter.
Stay at the Forefront of Bitcoin Innovation
Join our community of Bitcoin developers and enthusiasts to receive regular updates on Taproot Assets, implementation guides, and analysis of the evolving Bitcoin ecosystem. Be among the first to explore new opportunities in this expanding technology.