Bitcoin’s journey toward mass adoption faces two significant hurdles: scalability limitations and privacy concerns. The revival of Ecash—a concept pioneered by cryptographer David Chaum in the 1980s—offers promising solutions through two distinct implementations: Fedimint and Cashu. These protocols reimagine how Bitcoin can be used for everyday transactions while preserving privacy and reducing on-chain congestion.
In this comparison, we’ll explore how these modern Ecash implementations differ in their approach to trust, security, and usability—helping you understand which might be better suited for various use cases in Bitcoin’s evolving ecosystem.
Understanding Ecash: The Foundation of Both Solutions
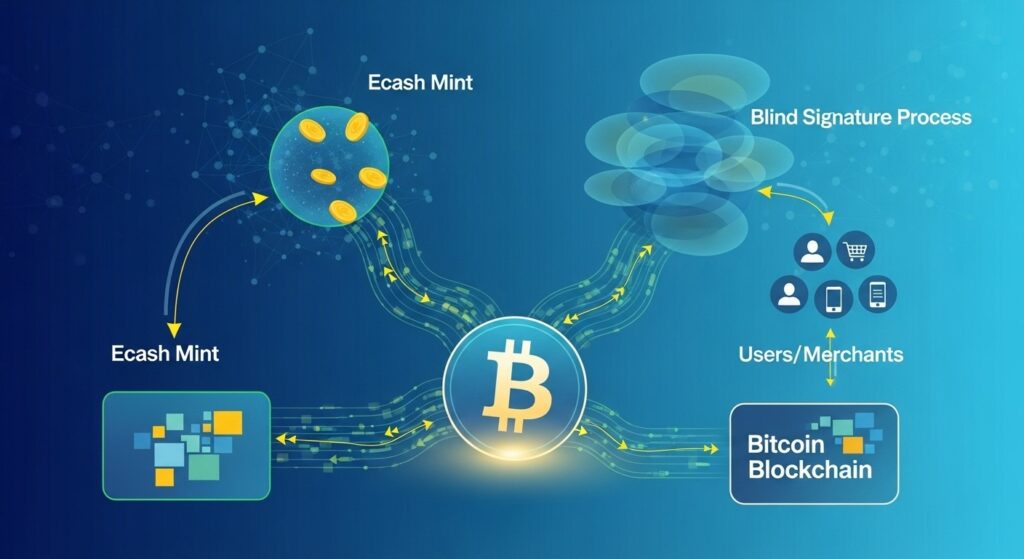
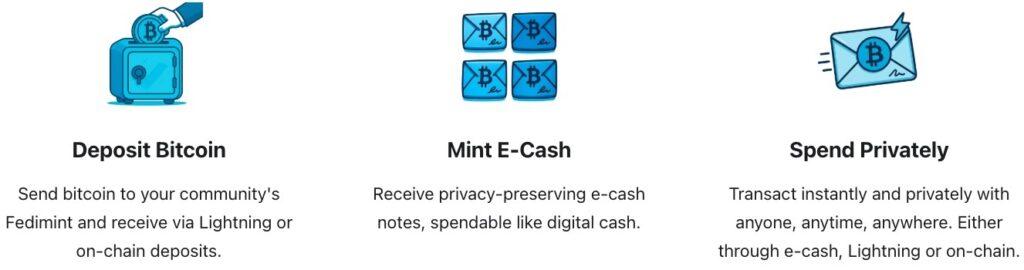
Before diving into the comparison, let’s establish what Ecash actually is. Developed by David Chaum in 1983, Ecash is a digital payment system that uses cryptographic techniques to ensure secure and private transactions. Unlike traditional digital payments that track user identities and transaction histories, Ecash operates through a mint that issues digital tokens in exchange for deposited funds.
The key innovation of Ecash lies in its use of blinded signatures—a cryptographic technique that allows the mint to verify and sign tokens without being able to link them to specific users or transactions. This creates a digital equivalent of physical cash, where transactions are:
Both Fedimint and Cashu implement this Ecash concept for Bitcoin, but they take fundamentally different approaches to the trust model that underpins the system.
Fedimint: Community-Based Federated Custody
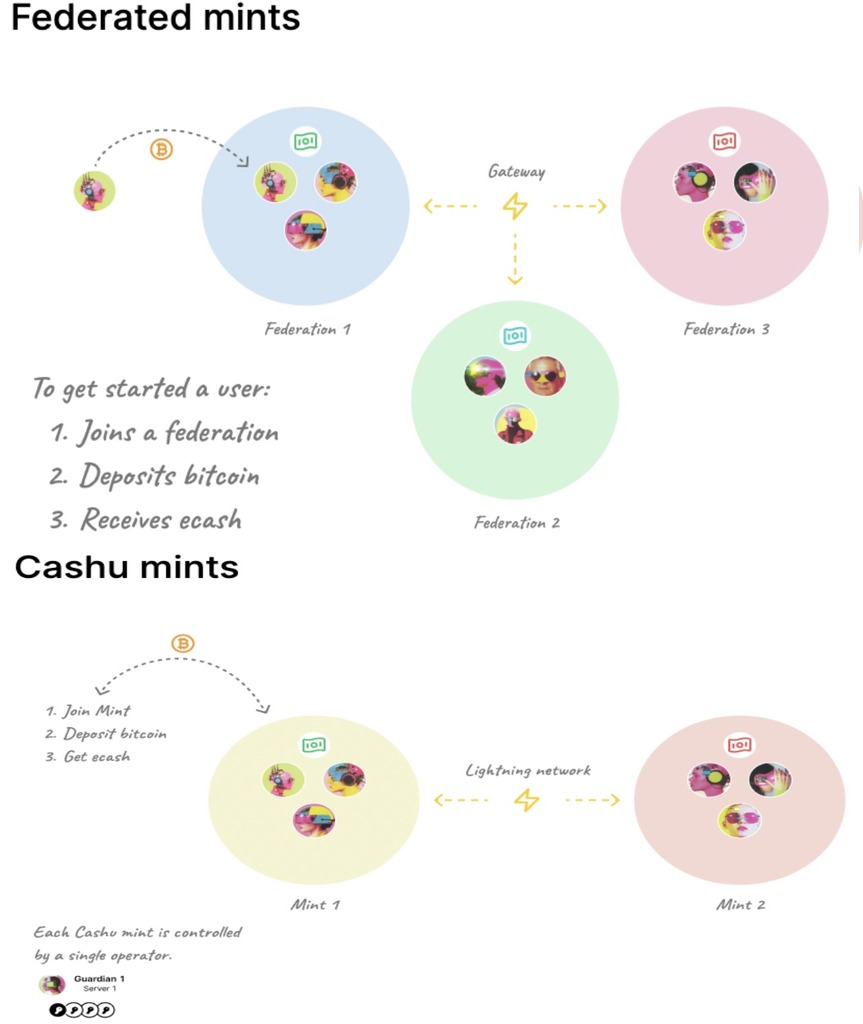
Fedimint represents a federated approach to Ecash, where trust is distributed among multiple guardians rather than concentrated in a single entity. The name “Fedimint” is a combination of “Federated” and “Mint,” highlighting its core design principle.
How Fedimint Works
In Fedimint, a group of trusted individuals (called “guardians”) collectively manage funds through a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus mechanism. This federation creates a multisignature wallet that holds the Bitcoin backing the Ecash tokens, ensuring that no single guardian can compromise the system.
Key Features of Fedimint
Trust Model
Fedimint employs a “shared responsibility” model where funds are secured by multiple guardians. For example, in a federation with four guardians, the system can withstand one malicious or compromised guardian without risking user funds.
Costs
Transactions within the federation are nearly free and instant since they happen off-chain. The primary costs are operational expenses for guardians (hardware, storage, and maintenance) and on-chain fees when depositing or withdrawing Bitcoin from the federation.
User Experience
Fedimint abstracts away the complexity of running Bitcoin and Lightning nodes, providing a simple interface for users. The federation handles all the technical aspects, allowing even non-technical users to benefit from Bitcoin’s capabilities.
Scalability
By batching multiple internal transactions into single on-chain operations, Fedimint significantly improves Bitcoin’s scalability. Hundreds or thousands of transactions can occur within the federation with only occasional settlement on the blockchain.
Advantages of Fedimint
- Enhanced security through distributed trust
- Resilience against individual guardian failures
- Suitable for organized communities and institutions
- Better protection against theft compared to solo mints
- Integrated Lightning Network support for external payments
Limitations of Fedimint
- Higher setup complexity for guardians
- Requires coordination among multiple parties
- More resource-intensive to maintain
- Still a custodial solution (though with safeguards)
- Federation must agree on protocol upgrades
Ready to explore Fedimint?
Discover how Fedimint can help your community build a more private and scalable Bitcoin experience.
Cashu: Lightweight Solo Mints
Cashu takes a different approach to Ecash implementation, focusing on simplicity and ease of deployment. Rather than relying on a federation of guardians, Cashu enables individuals to run their own “solo mints” or choose to trust existing mints based on reputation.
How Cashu Works
In the Cashu model, users deposit Bitcoin to a mint (usually via Lightning Network) and receive Ecash tokens in return. These tokens can be spent within the mint’s ecosystem or converted back to Bitcoin. The security of the system relies heavily on the trustworthiness of the mint operator.
Key Features of Cashu
Trust Model
Cashu relies on social trust and reputation. Users choose mints operated by individuals or organizations they trust, or they can run their own mint. This model emphasizes individual choice and social connections over technical safeguards.
Costs
Like Fedimint, internal transactions are nearly free. The operational overhead for running a Cashu mint is minimal, making it accessible for individuals and small businesses to set up their own mints.
User Experience
Cashu offers a straightforward experience with instant transactions. The lightweight nature of the protocol makes it particularly suitable for micropayments and everyday transactions within communities.
Scalability
Cashu achieves scalability through horizontal growth—many independent mints connected via the Lightning Network rather than scaling individual mints. This creates a network of interconnected but autonomous Ecash systems.
Advantages of Cashu
- Simple setup and maintenance
- Lower technical barriers to entry
- Ideal for micropayments and local communities
- Flexible deployment options
- Easy integration with existing services
Limitations of Cashu
- Single point of failure (the mint operator)
- Higher risk of mint operator absconding with funds
- Relies heavily on social trust and reputation
- Limited protection against technical failures
- Potential for fragmentation across many mints
Interested in Cashu?
Learn how to set up your own mint or find trusted Cashu providers for your Bitcoin transactions.
Head-to-Head Comparison: Fedimint vs Cashu
Now that we’ve explored both protocols individually, let’s directly compare Fedimint and Cashu across key dimensions to help you understand which might be better suited for different use cases.
| Feature | Fedimint | Cashu |
| Trust Model | Distributed trust among multiple guardians | Social trust in individual mint operators |
| Setup Complexity | Higher – requires coordination among guardians | Lower – can be set up by individuals |
| Security Model | Byzantine Fault Tolerant consensus | Reputation-based security |
| Resilience | Can withstand some guardian failures | Single point of failure |
| Ideal Use Case | Community banks, family offices, institutions | Individual merchants, micropayments, local networks |
| Scalability Approach | Vertical (larger federations) | Horizontal (more independent mints) |
Use Case Scenarios
When to Choose Fedimint
When to Choose Cashu
Practical Applications in the Ecash Revival
Both Fedimint and Cashu are enabling new use cases that weren’t previously possible with Bitcoin alone. Here are some real-world applications that showcase the potential of these Ecash implementations:
Community Banking
Fedimint enables communities to create their own banking systems, particularly valuable in regions with limited access to traditional financial services. Members deposit Bitcoin and use Ecash tokens for local commerce.
Merchant Payments
Cashu allows merchants to accept Bitcoin payments with better privacy and lower fees than traditional methods. Using tools like BTCPay Server with the Cashu plugin, businesses can easily integrate Ecash payments.
Gift Cards & Loyalty
Both protocols enable the creation of digital gift cards and loyalty points backed by Bitcoin. These can be transferred between users without requiring on-chain transactions, making micro-rewards economically viable.
Implementation Resources
If you’re interested in implementing either of these Ecash solutions, here are some resources to help you get started:
Fedimint Resources
Cashu Resources
Conclusion: The Future of Ecash on Bitcoin
The revival of Ecash through Fedimint and Cashu represents an important evolution in Bitcoin’s capabilities. Both protocols address critical limitations in scalability and privacy, though they take different approaches to the fundamental question of trust.
Fedimint’s federated model provides stronger security guarantees through distributed trust, making it ideal for communities and organizations that can coordinate multiple guardians. Cashu’s simplicity and ease of deployment make it accessible to individuals and small businesses looking for a lightweight solution.
Rather than competing directly, these protocols serve different needs within the Bitcoin ecosystem. Their development highlights how Bitcoin continues to evolve beyond its base layer, with layer 2 solutions addressing specific use cases while maintaining Bitcoin’s fundamental value proposition.